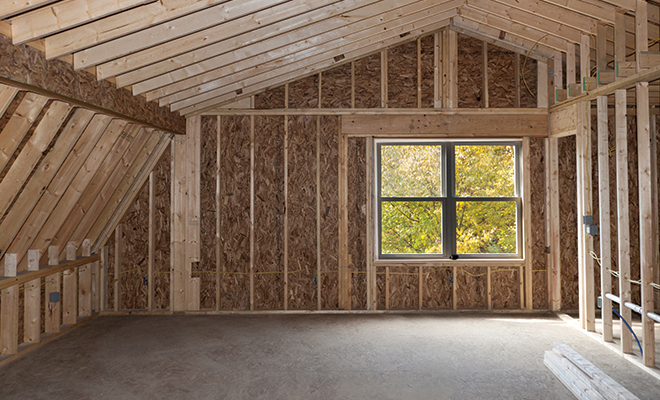
Choose green for building your home
Buildings have a major impact on the natural environment. In addition to depleting natural resources during construction, buildings consume nearly half of the energy produced in the U.S. each year. They also are responsible for nearly half of all CO2 emissions.
A builder’s choice of materials can go a long way in reducing a building’s environmental impact. More and more, commercial and residential builders are turning to green building materials that are sustainably grown, free from toxins and biodegradable. These materials are frequently harvested or produced locally. Besides being good for the outdoor environment, green buildings promote indoor air quality by reducing volatile organic compounds and other toxic gases that are emitted from many traditional building products.
Here’s an overview of some of the most popular green building materials.
Certified and sustainable woods
Wood seems like the most natural of building materials, but some wood products are greener than others. Builders who want eco-friendly wood look for products that are certified by the Forest Stewardship Council, an independent non-profit organization that promotes responsible management of forests throughout the world. Wood building materials that are Forest Stewardship Council-certified are guaranteed to be produced by companies that follow principles of responsible forestry.
Building materials made from sustainable wood often come from nontraditional sources. Cork, which is produced from the bark of a Mediterranean species of oak, is a sustainable product that can be harvested from living trees. Previously used mainly to make stoppers for wine bottles, cork is now being used for insulation, flooring and acoustical wall coverings. Many cork building products are made from remnants from the bottle-stopper manufacturing process, which wastes up to 70 percent of a tree’s bark. So using cork as a building material provides an additional recycling benefit.
Recycled and reused materials
Building materials made from recycled content consume fewer natural resources and typically require less energy to produce. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, one of the main sources of recycled content is industrial waste that replaces non-renewable virgin materials. For example, some builders spread shredded tires around building foundations in place of gravel to improve drainage.
Reused building materials are repurposed from existing buildings. They can be even more eco-friendly than recycled materials since they often require less processing before use. Reused materials are typically salvaged from buildings that are being demolished, so there’s an added benefit of reducing landfill use. Examples of reused building materials include old growth lumber, plywood, bricks, windows, plumbing fixtures, roofing tiles and architectural trim.
Green composite materials
Composite building materials are manufactured by combining two or more materials that have significantly different chemical or physical properties. With green composites, one or more of the materials may be recycled content. Most green composites are lightweight, which means they are less expensive to transport than steel, aluminum, concrete and brick. They offer high thermal insulation properties and are not prone to expansion and shrinkage as air temperature fluctuates.
Polymer matrix composites are a widely used green building material made from glass or carbon fibers combined with a grainy material such as sand or recycled glass. The two materials are bound together by a polymer, creating a long-lasting, extremely durable and low-maintenance green building material. Polymer matrix composites are used for plumbing, ductwork and roof and wall cladding.
Indoor air quality
Green building materials are expected to have a low impact on the environment throughout a building’s life cycle. This means that indoor air should be free of toxic substances. Building materials should emit a low level of carcinogens or none at all and should be resistant to moisture, since its presence encourages the growth of biological contaminants such as mold and mildew.
Many traditional building materials expose inhabitants to VOCs, which are a class of chemicals that vaporize into the atmosphere at typical indoor temperature and pressure conditions. Formaldehyde, toluene, benzene and other VOCs are found in composite wood products, insulation, paint, carpeting, sealants and adhesives. Low-VOC building materials have lower levels of vapor emissions, which benefits building inhabitants far into the future. According to green building experts, using low-VOC building materials is the most effective way to improve indoor air quality.
Where to find green building experts
Choosing the best green products for a building project can be tricky. Consider the case of bamboo, a renewable wood that is a green replacement for traditional oak flooring. In areas where native oaks are plentiful, however, reclaimed local oak may be a better choice than imported bamboo. To help builders solve this type of dilemma, organizations such as the U.S. Green Building Council have created useful checklists and guidelines. Visit BuildItGreen.org or BuildingGreen.com for more information about green building materials and green builders. Your local remodelers’ council or homebuilders’ association may also help you find experts close by. HLM
Sources: architecture2030.org, buildinggreen.com, epa.gov, inhabitat.com and usgbc.org.