Diamonds Are Forever
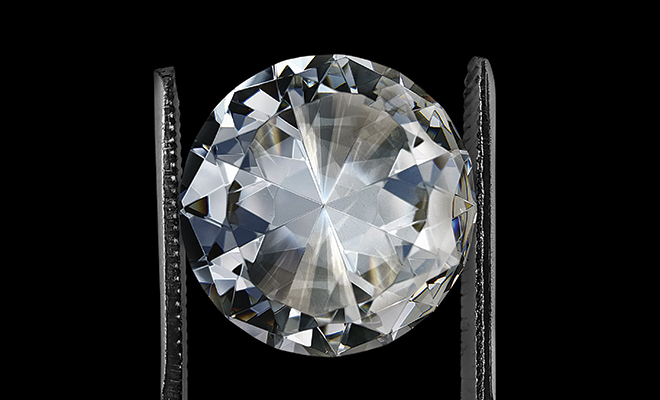
Are diamonds forever? Probably. Diamonds are the hardest natural substance on Earth and melt at temperatures of 5500° Celsius. No acid can destroy them and they can be cut only by other diamonds. Given the odds, diamonds will be around forever.
Until the 15th century, kings were the sole owners of diamonds. The power wielded by royals led others to curry favor in the form of beautiful and rare diamonds. The collections of many royal families or state jewel collections contain stones that are incomparable. Even so, many collectors around the world have beautiful diamonds in breathtaking collections.
Famous Diamonds
The Cullinan Diamond was an astounding 3,160 carats when it was first mined. It is the largest diamond ever discovered and was cut into the Star of Africa, an amazing 530.20 carats set in the British Royal Scepter, and the Lesser Star of Africa, an equally amazing 317.40 carats set in the Imperial State Crown of Great Britain.
The Golden Jubilee Diamond is the world’s largest faceted diamond. It is cut in a fire cushion shape and weighs 545.67 carats. The diamond is yellowish brown and currently part of the crown jewels collection in the Royal Thai Palace.
The Incomparable Diamond is golden and weighs 407.48 carats. In November 2002, the diamond was put up for auction on eBay for a reserve of 15 million pounds by an unknown owner. It did not sell.
The Oppenheimer Diamond is a yellow diamond weighing 253.7 carats uncut. It was donated to the Smithsonian Institution in 1964 by Harry Winston.
The Spirit of de Grisogono diamond is one of only three sizeable black diamonds in the world, weighing 312.24 carats. Its original weight was 587 carats; it is set in a white gold mounting with 702 smaller diamonds and is reported to have been privately sold.
The Lesotho Diamond is the 15th largest rough diamond ever discovered. In its uncut state, it weighs 603 carats and is rated a D.
The Four Cs
Diamonds are graded by several gemological institutes including the Gemological Institute of America, or GIA, the American Gem Society Laboratories and the European Gemological Laboratories.
The GIA was founded in 1931 by Robert M. Shipley of Wichita, Kansas. In the ’40s and ’50s, the GIA created a scale to grade diamonds that has since become accepted worldwide. The GIA’s diamond grading certificates evaluate diamonds for quality, not value. A specific diamond’s report includes scientific information on the Four Cs of quality—color, clarity, carat weight and cut—and includes proportion, finish and any known treatments. The price of a diamond does not depend on any one element, but rather it is a combination of all the Four Cs.
Color
Color can be the hardest to determine because of the wide range of colors on the market. Fancy diamonds may be pink, yellow, blue, brown, red and many other colors. The color scale runs from Z for obvious yellow to Grades D-E-F for a colorless type. Stones graded D-E-F are usually more expensive because of their rarity. Stones graded G-H-I-J are nearly colorless and may still be relatively expensive.
Fancy diamonds are graded on two scales, basic hue and intensity. If two stones have the same hue, clarity, shape and size, the more intensely-hued stone will be more expensive.
Some diamonds are treated by irradiation to change the basic hue to another color. They are a pleasant change from the pure, natural colorless stone and are much less expensive. However, they should never be considered an investment.
Clarity
Impurities or natural flaws in diamonds are called inclusions. These are caused by carbon deposits or small feather cracks created when the diamonds was formed. Using a 10X magnification, diamonds are graded from FL, flawless, to I1-I3, imperfect, based on the size, number, nature and position of the inclusions. The fewer inclusions found in a diamond the more expensive the stone will be. Flawless or Internally Flawless diamonds are very rare and expensive.
Carat Weight
The carat weight of a gemstone is simply its weight. One carat is 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. Thus, a diamond weighing 1.25 carats weighs 250 milligrams. In general, the price of a two-carat diamond will always be worth more than two one-carat diamonds, all other elements being the same.
Cut
The cut of a diamond is the most important factor in determining the brilliance and beauty of a diamond. Many different cuts are used on diamonds, but the standard round is probably the most popular and the one that commands the best price, all other factors being equal. Other popular shapes are the oval, pear, heart, marquis, emerald and princess. These cuts are called fancy cuts.
Whether you’re selecting a diamond for love, remembrance or investment, you can be assured that whatever your pleasure, diamonds are forever!
Sources: abazias.com, allcountries.org, diamondsafe.com, myjewelrysource.com, royal.gov.uk.